FEATURED ARTICLE
Tax Planning for Realized Gains and Ordinary Income
Tax planning strategies for realized gains and ordinary income

Tax planning strategies for realized gains and ordinary income

Tax planning helps you keep more of your realized gains by reducing your applicable taxes. Unfortunately, most people are unaware of how impactful tax planning could be and that it could boost their investment returns by 40% or more! The goal of tax planning is to make sure there is tax efficiency and it should be essential for anyone´s financial plans, but what exactly is it?
Tax planning is the process of analyzing and preparing a financial plan or a situation from a tax perspective that helps you to legally minimize how much you pay in taxes to help you keep more of your earned money, both for your use over time and to build your wealth for the long term.
We know there’s nothing simple about taxes, so Valur is here to help by taking the sophisticated tax planning and asset protection tools of the ultra-rich and making them seamless and accessible to everyone.
If you have received a large amount of income from selling an asset or just received a lot of income this year, Valur can help you set up the right tax planning structure for you. (Even if you’re still holding your assets and you’ve got a big gain coming, please check out our Unrealized Income Guide for details of this scenario)
In this guide, we’ll focus on the characteristics of five different structures commonly used for these situations, and we’ll also use an example to help you understand the benefits and the tradeoffs of each one.
Realized Income
Realized income is the appreciation that you receive as a result of a sale of any financial asset or from your salary. Critically, when you realize income you are subject to taxes.
On the other hand, unrealized gains are the potential profit (current price – the price you bought the asset at) that you would gain from selling any investment.
There are three key tax savings opportunities for realized income and salary that can help you reduce the taxes:
A tax credit is a dollar-for-dollar reduction in the amount of taxes you owe. For example, say you have $100,000 of income and owe $25,000 in taxes. If you then received a $5,000 tax credit, your tax liability would be reduced to $20,000, and you would take home that extra $5,000.
Tax credits directly reduce the amount of taxes you owe and in a sense are similar to a gift card or store credit you can use to reduce your tax bill. Over the last few years tax credits have become an increasingly popular tax mitigation tool due to increasing incentives tied to renewable energy incentives. In particular, the solar infrastructure credits in the 2022 Inflation Reduction Act are a particularly attractive opportunity to reduce your income tax. Read more about the IRA’s investment tax credits.
A tax deduction is another way to reduce taxable income, this time by reducing the income that is subject to taxation, thereby indirectly reducing the amount of taxes you owe. Contrast this with tax credits, which directly reduce the amount of taxes you have to pay.
Like tax credits, deductions are very common in the code. The most common is probably the deduction for charitable donations; by donating to a qualified charity, you can reduce your taxable income and thus your taxes. Some examples are Donating to Donor Advised Funds (DAF) and Setting up a Charitable Lead Annuity Trust (CLAT), both of which we’ll explain more in detail below.
Depreciation is the amount of value that a physical asset loses over time. When you drive your new car off the lot and its value drops immediately, or when a piece of machinery becomes less valuable due to wear and tear, that’s depreciation. From a tax standpoint, depreciation is relevant because you may be able to take a deduction for some or all of the amount of the value an asset loses over time, reducing your taxable income and saving money on your taxes.
Depreciation arises less often for wage earners than other deductions and tax credits, for the simple reason that this is typically not a deduction that you are allowed to take against wage income. Instead, depreciation usually arises if you have a business or own a rental property; business owners are allowed to deduct the depreciation on their business’s assets, like office furniture, electronics, and vehicles, and landlords may deduct the depreciation on the property they rent out.
Next, we are going to walk through a few popular tax planning structures used for realized gains:
The government offers 3 main benefits for individuals looking to buy qualified solar projects:
Solar projects typically include 15-25 year income streams tied to the energy produced by the project. These returns depend on the location of the project and local energy rates among other factors but typically will generate between 3-7% annually of your investment amount.
One of the most popular solar asset purchase structures is flip partnerships and sale-leasebacks. Below, we will explain how each structure works and their financial benefits, risks, and comparisons and you can also read our in-depth article about them here.
A flip partnership allows investors to receive a greater share of the tax credits and depreciation relative to their investment. The partnership is structured with three partners:
You can read about a real-life flip partnership case study here.
A sale-leaseback is a financial arrangement in which a solar project developer sells a solar system to an investor and then leases it back from the investor. This way, the investor benefits from tax incentives and a steady income stream from the project with minimal overhead, and the developer operates, maintains the system and is able to take the risk and make a profit based on the spread between the price they sell the electricity and what they pay the investor.
Credit risk: if the developer defaults on the lease payments, the investor may have to find another operator.
Need some help to understand which strategy is right for you?
Oil and gas well investments allow investors to put their money into the production and development of oil and gas wells. Investors can invest directly in a drilling operation or through partnerships that deal with the development and operation of wells, and this sector offers significant tax savings for high-bracket taxpayers.
CLATs are tax-exempt accounts that can earn you additional returns of 50% or more even if you’ve already sold your assets.
With a CLAT, you can:
With Grantor CLATs you gift assets to the trust and in exchange can receive a charitable deduction of up to 100% of your assets value to reduce your income that year. Every year, the trust gives a donation to charity and then you receive the remainder after that final contribution.
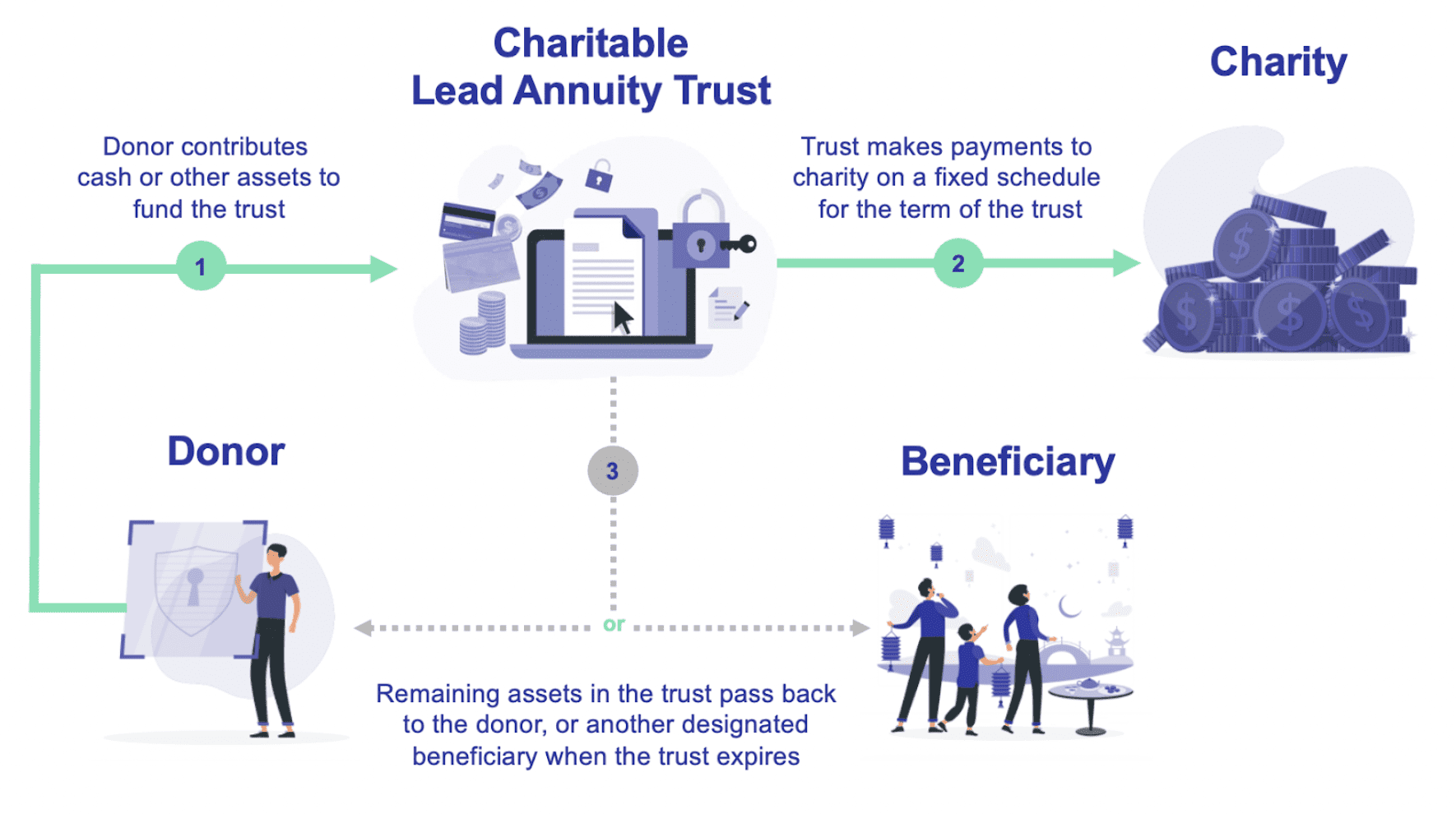
An important trade off for CLATs is that the money is locked away for the entirety of the trust’s term, much like a retirement savings account or IRA. At the same time, you are responsible for the taxes on the trust’s income, so this means that you may have to pay taxes on that income out of pocket each year. But this shouldn’t be a huge concern, as the amounts we’re talking about are small.
You can choose the length of your trust. Typically people set up CLATs for a minimum of 15- or 20-years to take advantage of the compounding tax mitigation benefits (depending, of course, on your assets, how quickly you expect your money to grow, and other details).
Interested in learning more about these structures? Visit our article where we explain how they work and in what sorts of situations they might prove valuable and check out your own potential tax savings with our online calculator.
In this video, Valur’s CEO, Mani Mahadevan, explains in-depth how to save more money with our tax planning strategies. Check it out!
Opportunity Zones are an economic development tool that allows you to invest in distressed areas in the United States and gain tax benefits.
Investments in Opportunity Zones are eligible for preferential tax treatment if they are made through a Qualified Opportunity Fund (QOF), which is an official designation for investment vehicles that commit to investing 90% or more of its assets in Qualified Opportunity Zones.
These structures can be a good fit if you have already realized a big capital gain. If you roll your eligible realized capital into a Qualified Opportunity Fund within 180 days of realizing the gain, two forms of tax incentive are available:
Capital gains rolled into a QOF may be deferred until the investment is sold or exchanged, or the end of 2026, whichever comes earlier.
You can save even more through an adjustment in cost basis of your investment. If you hold the QOF investment for at least 10 years, you can avoid taxes entirely on the sale of the Opportunity Zone investment.
The main downsides of Opportunity Zones include the following:
If you’d like to read more about Opportunity Zones, please visit our blog post on this topic here.
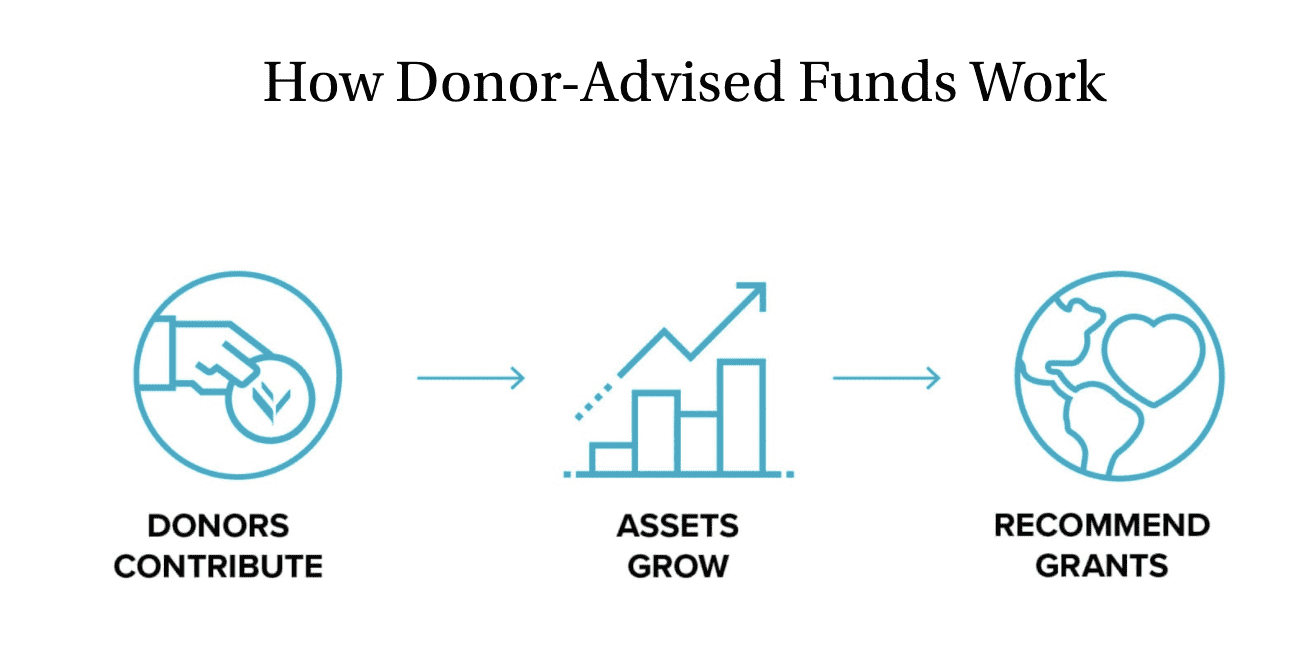
A Donor-advised Fund (DAF) is a giving account established at a public charity; it exists for the purpose of supporting charitable organizations, by offsetting or eliminating a big tax bill while retaining flexibility in timing and recipient of donations.
Donors can contribute to the fund as frequently as they like, and then recommend grants to their favorite charitable organizations whenever it makes sense for them.
The main benefits of DAFs are:
Downsides include the following:
As you might guess, each structure has its own set of positive and negative trade-offs. Choosing which structure to use is a personal decision that depends on your family circumstances, your financial goals, and what you want your life to look like for the next years.
There’s no “one size fits all” solution, and the right choice will be depend on your personal preferences and tax position. But don’t worry! Valur is here to help.
If you would like to learn more, please feel free to check out our Learning Center, or schedule a time to chat with us!
We’ve built a platform that makes advanced tax planning – once reserved for ultra-high-net-worth individuals – accessible to everyone. With Valur, you can reduce your taxes by six figures or more, at less than half the cost of traditional providers.
From selecting the right strategy to handling setup, administration, and ongoing optimization, we take care of the hard work so you don’t have to. The results speak for themselves: our customers have generated over $3 billion in additional wealth through our platform.
Want to see what Valur can do for you or your clients? Explore our Learning Center, use our online calculators to estimate your potential savings or schedule a time to chat with us today!
Ready to reduce your capital gains tax?
Free 15-min consult · No obligation · Capital Gains